Protective Relaying Terminologies Definition:
The various terminologies used in the protective relaying are,
- Protective Relay
- Relay Time
- Breaker Time
- Pickup
- Pickup Value
- Dropout or Reset
- Time Delay
- Sealing Relays or Holding Relays
- Current Setting
- Trip Circuit
- Phase Fault
- Earth Fault
- Phase Fault
- Protective System
- Unit Protection
- Reach
Protective Relay
This is a master mind control of an electrical relay, which closes its contacts when an actuating quantity (the value of incoming current or voltage) reaches a certain preset value. It contains some mechanical switch i.e closing contacts and opening contacts typically NO and NCs. Due to closing of contacts, relay initiates a trip circuit of circuit breaker or an alarm circuit.
Relay Time:
Each relays are having its own characteristics. The time between the instant of fault occurrence and the instant of closure of relay contacts. As per Government rule, we should calibrate each relay to find out the relay time.
[wp_ad_camp_1]
Never Forget to see: Relay section Explanation
Breaker Time:
It is the time between the instant at circuit breaker operates and opens the contacts, to the instant of extinguishing the arc completely.
Fault Clearing Time:
The total time required between the instant of fault and the instant of final are interruption in the circuit breaker is fault clearing time. It is sum of the relay time and circuit breaker times.
Pickup :
A relay is said to be picked up when it moves from the OFF position to ‘ON position. Thus when relay operates it is said that relay has picked up.
Pickup Value:
It is the minimum value of an actuating quantity at which relay starts operating, in most of the relays actuating quantity is current in the relay coil and pickup value of current is indicated along with the relay
Dropout or Reset:
A relay is said to dropout or reset when it comes back to original position ie. when relay contacts open from its closed position. The value of an actuating quantity current or voltage below which the relay resets is called reset value of that relay.
Time Delay:
The time taken by relay to operate after it has sensed the fault is called time delay of relay. Some relays are instantaneous while in some relays intentionally a time delay is provided.
Sealing Relays or Holding Relays:
The relay contacts are designed for light weight and hence they are therefore very delicate. When the protective relay closes its contacts, it is relieved from other duties such as time lag, tripping etc. These duties are performed by auxiliary relays which are also called sealing relays or holding relays 10.
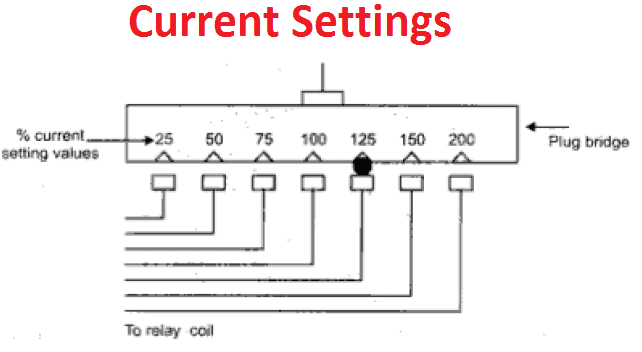
Current Setting:
The pickup value of current can be adjusted to the required level in the relays which is called current setting of that relay. It is achieved by use of tapings on the relay coil, which are brought out to a plug bridge as shown in the Figure. The tap values are expressed in terms of percentage full load rating of current transformer (C.T) with which relay is associated.
[wp_ad_camp_1]
Also see: What is voltage transformer
Trip Circuit:
The opening operation of circuit breaker is controlled by a circuit which consists of trip coil, relay contacts, auxiliary switch, battery supply etc. which is called trip circuit
Earth Fault:
The fault involving earth ie called earth fault. The examples of earth fault are single line to ground fault, double line to ground fault etc. More about Earth fault
Phase Fault:
The fault which does not involve earth is called phase fault. Example: Line to Line Fault
Protective Scheme:
The combination of various protective systems covering a particular zone for a equipment is called protective scheme. For example a generator may be provided with protective systems like overcurrent, differential, earth fault etc. The combination of all these systems is called generator protective scheme
Protective System :
The combination of circuit breakers, trip circuits, CT. and other protective relaying equipments is called protective system.
Unit Protection:
A protective system in which the protection zone is clearly defined by the C.T. boundaries is called unit protection. Such systems work for internal faults only
Reach:
The limiting distance in which protective system responds to the faults is called reach of the protective system. The operation beyond the set distance is called over-reach while failure of distance relay within set distance is called under-reach.









![What is Arc Chute? Types, Working Principle [Video Included] arc chute working priciple](https://electrical4u.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/arc-chute-218x150.png)

Very educative