What is MPCB?
MPCB is nothing but a Motor Protection Circuit Breaker. It contains thermal overload protection, short circuit fault protection, unbalance load, and phase loss fault protection. Motor Protection Circuit Breaker is a widely used circuit breaker for both static and dynamic electrical equipment.
The reliability of the MPCB greater than MCCB or fuse. Typically, MPCB > MCCB > Fuse.
However, in this article, we are going to study the construction, working principle of MPCB, advantages, disadvantages, and Application.
Construction of Motor Protection Circuit Breaker:
Construction front, MPCB contains 6 different parts such as thermal overload release, magnetic trip unit, main contact, auxiliary switches, arc chute, plunger, and enclosure.
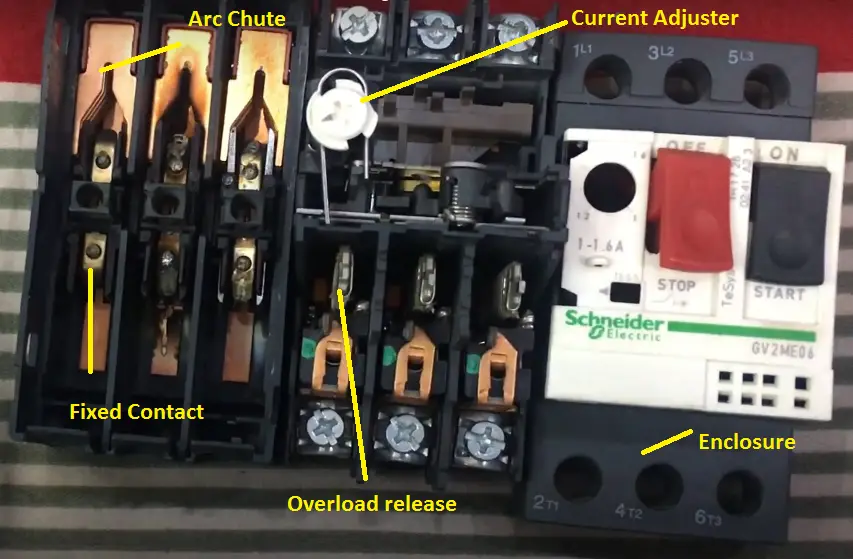
Thermal Overload release:
Thermal overload release is a protection that is used to protect the motor from overload or high balanced current which is more than a preset value.
The thermal overload is designed along with the current adjuster to limit the current flow to the motor. It is made up of bimetallic strip (usually steel and copper, or in some cases steel and brass). It operates when the current flow is higher than the preset value.
The current adjuster is nothing but a spring mechanism that increases or decreases the distance between bimetallic contact and operating mechanism. i.e when you increase the current flow through the mpcb, the adjuster increases the distance between the bimetallic strip on the operating mechanism. The same precisely set in the manufacturer laboratories.
Magnetic Trip:
The magnetic strip is a short circuit fault protective mechanism. Three number of the current transformer will be placed at the outgoing terminal. A plunger will be placed inside of the CT. Under normal conditions, the current transformer’s plunger does not operate the tripping mechanism.
Main Contact:
The main contacts of the Motor Protection Circuit Breaker are responsible for the current flowing from the source to the load circuits. It is divided into two-part fixed contacts and moving contacts.
Both contacts are made up of Copper tungsten and copper tungsten carbide. The fixed contacts will be stabled at the MPCB enclosure and moving contact will be fixed with the trip mechanism.
Arc Chute:
Arc chute is used to quenching the arc developed at that time of MPCB circuit is opening. The outer body It is made up of glass sole to withstand high temperature during the circuit breaker is opening. The arc chute contains copper plates to cut the continuity of the arc.
Auxiliary switches:
Auxiliary switches are the NO or NC and which is used to send the MPCB status to the external circuits.
Enclosure:
An insulative enclosure is used to cover the inner mechanism from the outside world. It is made up of molded plastic resins. To increase the strength, the enclosure, fillers such as glass fibers are added to the plastic resin.
Working Principle of Motor Protection Circuit Breaker:
Under normal condition, it does not trip the circuit. Let see the working principle:
Overload tripping:
As you know, each conductor has some resistance. So as the current passes through that conductor causes power loss in terms of heat. The heat produced in the conductor is directly proportional to the value of the current.
Hence the bimetallic strip is designed to bend the particular value of the current. Under normal conduction, the strip releases a small amount of heat and it bends slightly. During the high current, the strip bends higher and touches the tripping mechanism.
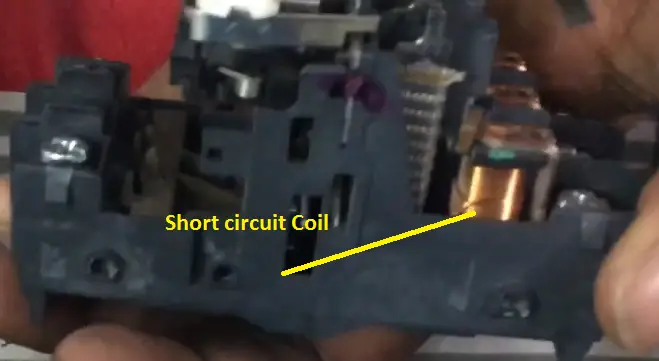
Short circuit:
The short circuit fault will be cleared by the magnetic trip. Some advance MPCB comes with the individual current transformer and the primary will be connected in series with the main.
The CT reads the exact current flow and under short circuit fault condition, the CT reads higher current. It sends the tripping signal to the tripping coil and the coil pulls the plunger associated with the tripping mechanism.
Unbalance & Phase loss protection:
Note that, the MPCB’s unbalance protection does not work immediately, it is depending upon the current level. It is a very simple concept that while decreasing the voltage the current will increase.
Example: Consider, a motor’s one of the phase wire has lost. Then all the load shall forward to the remaining phase hence the remaining phase shall carry the extra load from 100% to 150%. Due to this higher load, the MPCB thermal overload trips the circuit.
Advantages:
- The high degree of protection such as Short circuit, Unbalanced, phase loss, and over current protection are available in one pack.
- Easy adjustment
- Compact size
- Less maintenance
- No need for external thermal overload relay
Disadvantage:
- High cost. Example: 45 – 63 A Siemens make MPCB cost around Rs 45,000 INR ($750 USD)
- Cannot be repaired (use & through).
- Cannot adjust the short circuit current tripping limit
Application:
- Induction Motor starting (DOL/Star-delta).
- Lighting circuit applications
- Direct starting applications
Motor Protection Circuit Breaker Selection:
It is available from 0.1 Amps to 630 Amps. It does not have any range selection option for short circuit protection. I have used up to 400 Amps Motor Protection Circuit Breaker for 160 kW motor.
Max MPCB Current Range in Amps = 1.6 x 1000 x P(kW) / (1.732*Volts*pf)
Example:
Select the MPCB rating for a three-phase, 415V, 0.8pf, of 10HP/7.5kW induction motor
MPCB Range in Amps = 1.6 x 1000 x 7.5 / (1.732*415*0.8)
= 20 Amps
Then you have to choose the MPCB range between 13 A-22 Amps. Such range MPCB can be used for the next level of the motor also. i.e 11kW Motor. The 11 kW motor Full load Amps is 21 Amps. It will be within the range of the MPCB 22Amps
Siemens MPCB:

Siemens make has the following advantages
- In a smaller range, it does not have any trip indications. We cannot find any difference between OFF and Trip.
- Rough use
- Less wear and tear against short circuit.
ABB make Advantages:

It has some advantages like Siemens but the main disadvantage is that ABB MPCB has a frequent failure of the trip resetting mechanism. In fact, I have replaced around 25 number of ABB make within two years due to resetting mechanism failure and break down.


![What is Normally Open & What is Normally Closed [Video Included] What is NO and NC](https://electrical4u.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/What-is-NO-and-NC-218x150.png)






Is an MPCB & contactor nessessary..
E. G For 1kw motor with timer, is it enough to connect timer to contactor and motor to contactor – or should you always fit the MPCB powered from contactor (timer Live drives contactor which powers MPCB, motor connected to MPCB?