Air Conditioner (A/C) Working Principle
Air conditioner gives you much thermos comfort during summer season and which maintains our room temperature at the optimum level. They also help us to remove airborne particle and humidity in the room. In this article, we are going to discuss about the basic working principle of air conditioner.
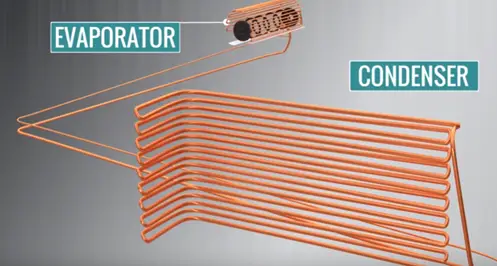
Air conditioner has two connected coils such as evaporator and condenser, refrigerant fluid, compressor, exhaust fan, connection copper tube, expansion value, Stabilizer, thermister etc.
Before understanding the working of air conditioner, just remember our full body functionality. the refrigerant is work as blood of the air conditioner and Compressor as heart, condenser as waste digestion system.
Working Principle of Air Conditioner:
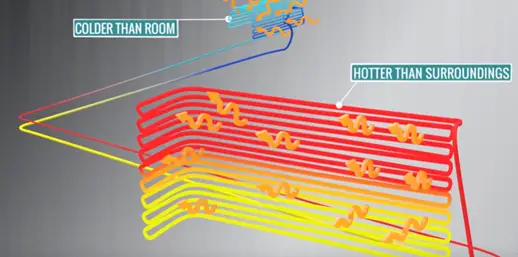
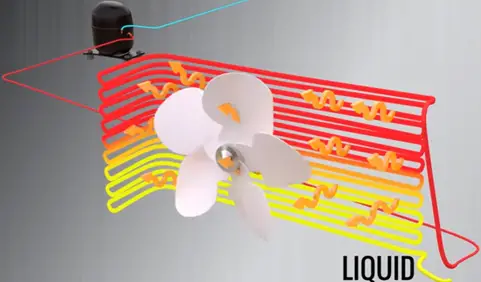
The fundamental principle of air conditioner is, just keep the evaporator in colder condition than room temperature. In such way that, condenser will be hotter than surroundings.
With this condition continuously flowing fluid (refrigerant) obliviously observed the heat from the room and ejected out to the surroundings. This is the fundamental working principle of the air conditioner.
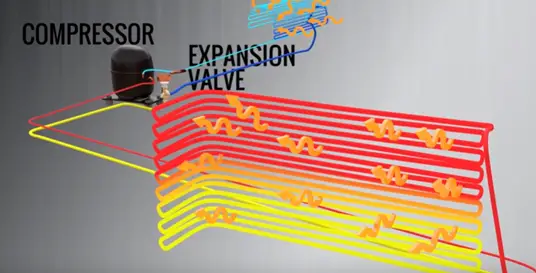
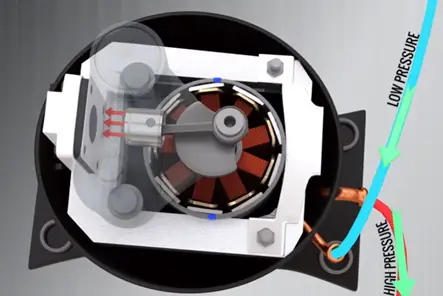
The compressor tackles the refrigerant in its gaseous state so that while compressing the gas, the temperature rises along with the pressure.
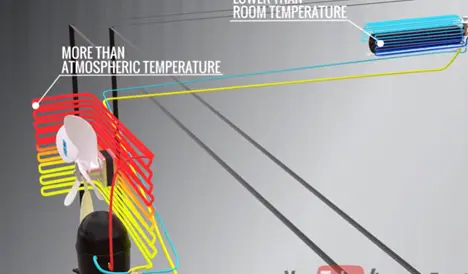
The temperature at the compressor outlet will be for higher than the atmospheric temperature. Therefore if you pass hot gas condenser heat exchange will easily eject the heat by forced cooling. Here an exhaust fan in the condenser unit makes this easier.
During this heat will be ejected by the condenser, This condensed gas will pass into a liquid expansion valve which is fitted at the exit of the condenser.
Here the net out let pressure of the condenser is lower than the net inlet pressure of the condenser.
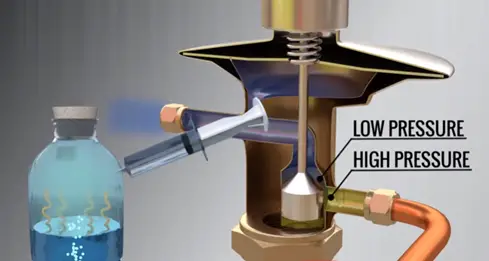
What is The Purpose of Expansion Valve in Air Conditioner?
The purpose of the expansion valve is used to restrict the refrigerant (R22) flow and reducing the pressure of the fluid.
The expansion valve works, “we can boil the liquid by reducing the pressure around it”. This principle works inside of the expansion valve as the pressure drops one part of refrigerant liquid starts evaporating.
However to perform this evaporation, some energy to be supplied; this energy comes from the refrigerant.
So its temperature drops and finally we gets low temperature refrigerant inside of the air conditioner. Also note, This low temperature should be lower than the added room temperature it means New Refrigerant temperature < Room temperature + Old Refrigerant temperature.
So by passing the room’s air over the evaporator coil (Indoor Unit), the room temperature will drop. The refrigerant gets converted into vapor during this heat absorption process.
In modern compressor use scroll compressor in the reciprocating type. These compressor are silent and they have good speed control.
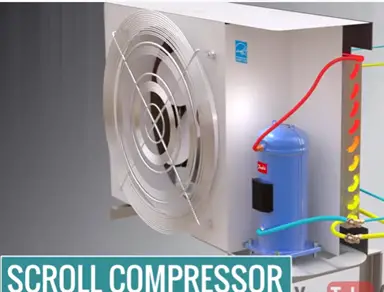
For better temperature control just by adjusting the motor speed, compressor speed, refrigerant flow rate and cooling capacity controlled accurately.
Intersecting design for air conditioner, the compressor of the air conditioner is designed to handle only vapour and small fraction of a liquid content affects its performance and damage the compressor. For these reason the evaporator control all of the liquid to vapour and even increases the temperature of the vapour by 5 to 8 degree Celsius after the conversion. This makes fluid which enters the compressor is purely vapour.
This condition is maintained by a special kind of expansion valve called thermostatic expansion valve (TXV)
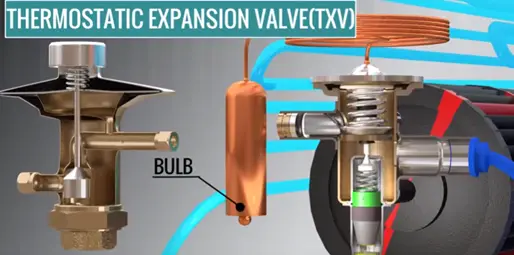
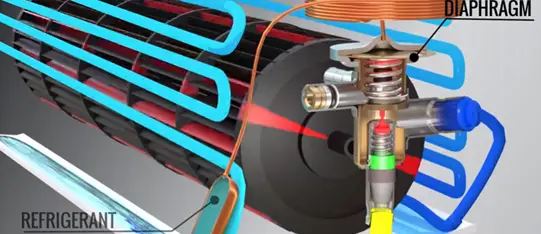

Thus evaporator will receive much cooler fluid and absorb a great amount of heat. This will make sure that all the liquid will converted into a vapour, the complex tank of the vapour having the vapour condition is automatically maintained by TXV.
Why Air Conditioner Unit is Ton:
What is ton?
Ton is the unit which is associated with air conditioner. The ton represents how much heat evaporator can absorb from the room. In simple words represents in air conditioner heat removable capability.
1 TON= 3517 W or 12000 BTU (British Thermal Unit), 1 BTU=1,055 joules. The temperature is lower in room temperature in the coil inside the room. Then the temperature is more than atmospheric temperature in the coil outside the room.
Image/Content Credit: Learn Engineering





It is a nice blog post.