Zinc Iodide
Zinc iodide is an inorganic compound that has the composition of zinc and iodine. It will be exists in the both anhydrous and dehydrate form. Zinc iodide is the ability to absorb the water from the atmosphere. It can be catalysed for the conversion of methanol to triptane. It is a strong base. It has considered zinc as the cations and iodide as the anions. It is directly reacted with the oxidizing agent. The systematic IUPAC name is known as zinc iodide. The chemical or molecular formula of zinc iodide is ZnI2. It is also known as zinc (II) iodide.
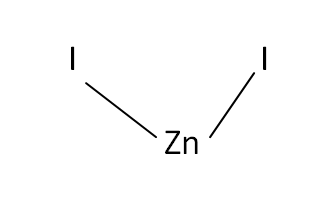
Structural Formula
This is the structural formula of the zinc iodide:
Chemical Formula
The chemical formula of the zinc iodide is ZnI2.
Preparation Method
The zinc iodide is prepared as the follows. In an aqueous solution, the zinc is reacted with the iodine along in the water it gives the formation of zinc iodide. It has cluster with the oxygen atoms with the double bonded covalent. It coordinated as the three dimensional structure at the point of vertices.
Zn + I2 → ZnI2
Physical Properties
| Melting point | 446C |
| Boiling point | 1150C |
| Molecular weight | 319.22g/mol |
| Density | 4.74g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | 450g/100mL(20C) |
| Refractive index | 1.43 |
| Crystal structure | Tetragonal |
| Magnetic susceptibility | -98.0×10-6cm3/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
Chemical Properties
Zinc iodide is the tetragonal in structure and a white solid in the appearance. It is highly reactive agent that has damaged the particles. The boiling point is high and the melting point is low. It is soluble in the water. it has low density and high molar mass. The magnetic suspectibility is very low.
Uses
Zinc iodide is a catalyst that is convert methanol to triptane. It is also used as a stain in microscopy. It is take the X-ray for detecting the diseases with the clear image.