Zinc Carbonate
Zinc carbonate is commonly known as the smithsonite or zinc spar. It is the mineral ore of zinc and presenting as a secondary material for the zinc bearing ore deposits. It is an inorganic compound and insoluble in water. It is bonded to six Zn centres that could be coordinate. It is slightly soluble in the alkalis, acids and ammonia. Both the minerals has present at the leads to the confusion of the alcoholic compound. The systematic IUPAC name is known as zinc carbonate. The chemical or molecular formula of zinc carbonate is ZnCO3.
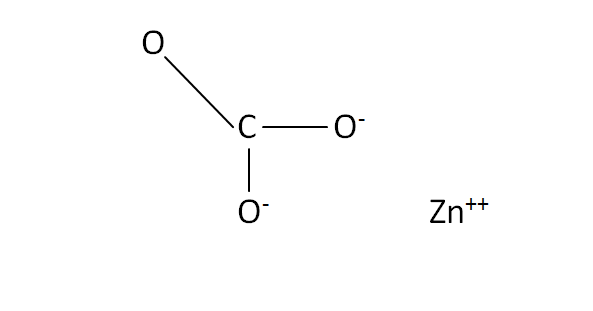
Structural Formula
This is the structural formula of the zinc carbonate:
Chemical Formula
The chemical formula of the zinc carbonate is ZnCO3.
Preparation Method
In the hydrothermal synthesis process the zinc chloride is reacts with the potassium carbonate that forms the zinc carbonate and potassium chloride as the byproduct.
ZnCl2 + K2CO3 → ZnCO3 + 2KCl
Physical Properties
| Melting point | 1970C |
| Boiling point | 333.6C |
| Molecular weight | 125.38g/mol |
| Density | 4.434g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | 0.91mg/L |
| Refractive index | 1.848 |
| Crystal structure | calcite |
| Magnetic susceptibility | -34×10-6cm3/mol |
Chemical Properties
It has high density to produce the cosmetics. It is highly stable chemical compound and greatly sustained in the molecular weight. The refractive index is very high in the crystal structure of the calcite compound. It is highly inflammable substances and being productive from the hazardous materials. By the calcinations process it can be achieved through the formation of zinc oxide and carbon dioxide.
Uses
Zinc carbonate is usually used in iron and steel to protects dilopidation. It is also used in painting and agriculturally stuff. It is used for astingent and absorbent. This carbonate is also termed as the calamine. Calamine is very oil treatment of pruritus. This natural product is zinc carbonate with small quantity of iron oxide. This is also present in zinc anodes which is used in television monitor and lighting. It is occur in both inhaling and fumes and particles.