Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate is an inorganic compound that has the combination of potassium and dihydrogen ion. It is a well buffering agent. It is mainly used for the manufacturing the fertilizers. These potassium is highly effective chemical compound and we can easily enumerate the properties of the potassium dihydrogen phosphate. It reacts with the other chemical compounds and some are no chemical reactions. The systematic IUPAC name is known as potassium dihydrogen phosphate . The chemical or molecular formula of potassium dihydrogen phosphate is KH2PO4. It is also known as monobasic potassium phosphate.
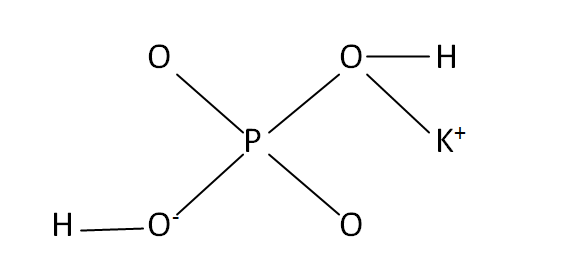
Structural Formula
This is the structural formula of the potassium dihydrogen phosphate:
Chemical Formula
Chemical formula of the Potassium dihydrogen phosphate is KH2PO4.
Preparation Method
When the potassium is reacted with the phosphate and it gives the formation of the potassium dihydrogen phosphate. It could be the loss of water at 400C, it will form the metaphosphate. It gives the piezoelectric effect when the monopotassium phosphate is above the ordinary temperatures. At that point the distorting force is directly proportional to the emf.
Physical Properties
| Melting point | 252.6C |
| Boiling point | 400C |
| Molecular weight | 136.086g/mol |
| Density | 2.338g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | soluble |
| Refractive index | 1.5093 |
| Crystal structure | White tetragonal crystals |
| Magnetic susceptibility | -20.1×10-6cm3/mol |
| Appearance | White granule powder |
Chemical Properties
The melting and the boiling point is equally balanced. It looks like a white granule powder in the appearance. The range of magnetic susceptibility is above 10 and it is white tetragonal crystals in the structure. It has low density and moderate molecular weight. It is soluble in the water.
Uses
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate is used for buffering agent in fertilizers. It is mixed in ammonium phosphates and urea in fertilizers to minimize the escape of ammonia.