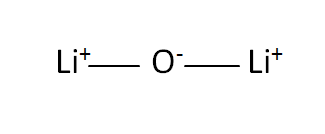Lithium Oxide
Lithium oxide is an inorganic compound which is a white solid with the pure crystalline form. It is evaluated by the amount of lithium oxide is presented. These chemical compounds reacted with the water violently to form the lithium oxide. A spodumene is the principal mineral of lithium. It can be decomposed at the temperature between 300-400C. The systematic IUPAC name is known as lithium oxide. The chemical or molecular formula of lithium oxide is Li2O. It is also known as Lithia.
Structural Formula
This is the structural formula of the lithium oxide:
Chemical Formula
The chemical formula of the lithium oxide is Li2O.
Preparation Method
When the lithium metal is heated with the atmosphere air and mixed with the oxygen which is present in the air is reacted and form the chemical compound is called lithium oxide. It is produced at the temperatures is above 100C. the lithium oxide has a linear bond length with the strong ionic bonding in the ground state gas phase. In the thermal decomposition at the temperature of 450C to form the lithium peroxide. The chemical reaction is given as follows.
4 Li + O2 → 2Li2O
Physical Properties
| Melting point | 1570C |
| Boiling point | 2600C |
| Molecular weight | 29.88g/mol |
| Density | 2.013g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | Reacts vigorously to form LiOH |
| Refractive index | 1.644 |
| Crystal structure | Antifluorite(cubic) |
| Magnetic susceptibility | -18.5×10-6cm3/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
Chemical Properties
Lithium oxide is corrosive material and reacts violently with the water. it is a non inflammable substances. it is related to organic chemistry. It is antifluorite in structure. It looks like a white solid in the appearance. The boiling point is high and the melting point is low. It has low molar mass and high density.
Uses
Lithium oxide is used for producing flux ceramic glazes. It is thickening agent so it make of greases and in the coolant nuclear reactors. The lithium batteries are manufacturing by using the chemical substances.