Calcium Acetate
Calcium acetate is an inorganic compound that has white hygroscopic solid in nature. It has consists of calcium as cations and acetate as anions. It has a strong reducing agent and which is mildly basic compound. Calcium acetate is soluble in water and insoluble in various organic solvents. The systematic IUPAC name is known as calcium acetate. The chemical or molecular name of calcium acetate is C4H6CaO4. It is also known as acetate of lime or calcium ethanoate.
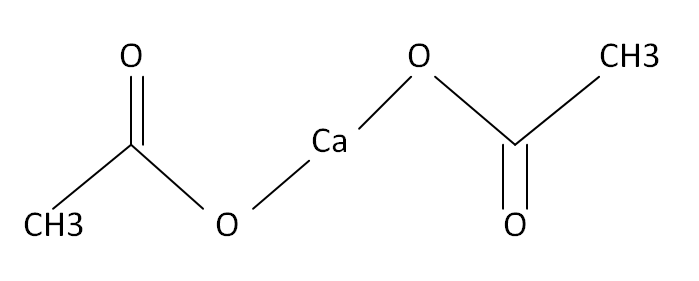
Structural Formula
This is the structural formula of the calcium acetate:
Chemical Formula
The chemical or molecular formula of the calcium acetate is C4H6CaO4.
Preparation Method
The calcium acetate is prepared when it is reacting with calcium carbonate and vinegar. It allows the precipitation of the product when it is ready to dissolve in water on the aqueous form. It is an exposure to the thermally unstable. It is insoluble in acetones and ethanol. The chemical reaction is given as follows.
CaCO3 + 2CH3COOH → Ca(CH3COO)2 + H2O + CO2
Physical Properties
| Melting point | 160C |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| Molecular weight | 158.166g/mol |
| Density | 1.509g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | 37.4g/100mL |
| Refractive index | 1.55 |
| Crystal structure | Monoclinic |
| Magnetic susceptibility | -70.7×10-6cm3/mol |
| Appearance | White solid hygroscopic |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in methanol, hydrazine. Insoluble in acetone, ethanol and benzene. |
| Odor | Slightly acetic acid odour |
| Acidity | 0.7 |
Chemical Properties
Calcium acetate is a non inflammable substances. It is more hazardous to the environment. The boiling point is decomposed and the melting point is low. The acidity of the calcium acetate is less than 1. It is monoclinic in structure. It looks like a white hygroscopic solid in the appearance.
Applications
Calcium acetate is used as a food additive. It is mainly used for manufacturing of lubricants. It is used as a corrosion inhibitor. It is widely used for making of agricultural products.