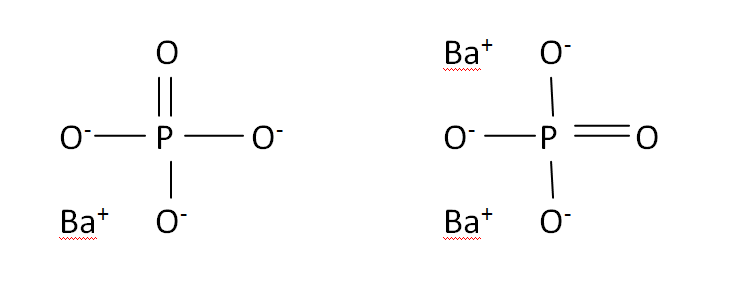Barium Phosphate
Barium phosphate is an inorganic salt compound that has consists of barium and phosphate. Generally it has a colourless solid which is similar to the acetic acid. The barium phosphate is considered as the 3 cations and 2 anions. It has been linked to the sharing oxygen atom with the structural formula. The systematic IUPAC name is known as barium phosphate. The chemical or molecular name of barium phosphate is Ba3(PO4)2. It is also known as tribarium diphosphate.
Structural Formula
This is the structural formula of the barium phosphate:
Chemical Formula
The chemical formula of the barium phosphate in Ba3(PO4)2. It has cosists of three barium and diphosphate and oxygen ions.
How it is Prepared
When the barium carbonate is reacted with the metaphosphoric acid it gives the product of barium phosphate and carbon dioxide, water is the byproduct. It can be precipitated and slowly removed from the cations. It could be commonly involved in the aqueous solution and that has been in the anhydrous form. The chemical reaction is given as follows.
BaCO3 + 2HPO3 → Ba(PO3)2 + CO2 + H2O
Physical Properties
| Melting point | 1560C |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| Molecular weight | 295.27g/mol |
| Density | 3.63g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | Soluble |
| Refractive index | 1.540 |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Solubility | Insoluble in alcohol. |
| Complexity | 36.8 |
Chemical Properties
Barium phosphate is a non inflammable substances and a white powder in the appearance. It is highly reactive agent that has damaged the particles. The boiling point is decomposes and the melting point is high. It is soluble in the water and insoluble in alcohol. It has low density and high molar mass. The complexity is 36.8.
Applications
Barium phosphate is used for pulsed laser and glass production. It is inflammable. It can cause eye and skin irritation. It is uses as the proton conducting material in the fuel sensors.