Barium Acetate
Barium acetate is a chemical compound that has consists of salt of barium and acetic acid. It is highly soluble in water and used as a cationization agent. It decomposed the carbonate when its heating at the room temperature. The systematic IUPAC name is known as Barium acetate. The chemical or molecular formula of Barium acetate is C4H6BaO4.
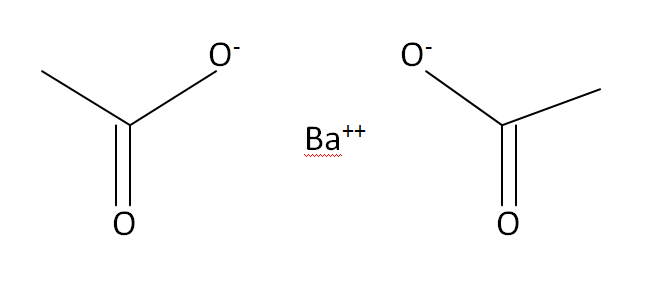
Structural Formula
This is the structural formula of the Barium acetate:
Chemical Formula
The chemical formula or molecular formula of Barium acetate is C4H6BaO4.
Preparation Method
When the barium carbonate is reacted with the acetic acid it forms the barium acetate and the carbon dioxide and water as the byproduct. Further it is heated above 41C. at that time the barium sulfide can be used to reacting with the acetic acid to form the barium acetate and hydrogen sulfide as the byproduct. This solvent is evaporated off and the barium acetate crystallized.
BaCO3 + 2CH3COOH → Ba(CH3COO)2 + CO2 + H2O
BaS + 2CH3COOH → Ba(CH3COO)2 + H2S
Physical Properties
| Melting point | 4500C |
| Boiling point | 221.20C |
| Molecular weight | 255.43g/mol |
| Density | 2.468g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | Soluble |
| Odor | odorless |
| Crystal structure | Tetragonal |
| Magnetic susceptibility | -100.1×10-6cm3/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
Chemical Properties
The melting point is very high and it is insoluble in acetone. It is tetragonal in structure. It looks like a white solid in the appearance. The density is low and medium molecular weight. It is odourless and the magnetic susceptibility is balanced.
Uses
Barium acetate is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis. It is also used in preparation of other acetates. It is widely used in printing textiles,varnishes and dry paints.