Peak to Peak Voltage Calculator:
Enter the value of RMS voltage, VRMS(V) to determine the value of Peak to peak voltage, Vp-p(V).
Peak to Peak Voltage Formula:
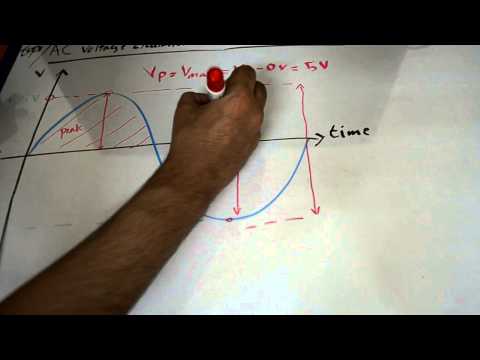
Peak-to-Peak Voltage is a vital concept in electrical and electronics engineering that represents the total voltage swing from the maximum positive point to the maximum negative point of a waveform.
It is an essential parameter in systems where signal integrity and amplitude are critical, such as in audio processing, radio frequency communications, and oscilloscope measurements.
The peak-to-peak voltage is particularly useful when analyzing waveforms that are sinusoidal, as it gives a comprehensive view of the voltage variation throughout a cycle.
Peak to peak voltage, Vp-p(V) in volts is calculated by multiplying the 2.828427 by RMS voltage, VRMS(V) in volts.
Peak to peak voltage, Vp-p(V) = 2.828427 * VRMS(V)
Vp-p(V) = peak to peak voltage in volts, V.
VRMS(V) = rms voltage in volts, V.
Peak to Peak Voltage Calculation:
- Calculate the Peak-to-Peak Voltage Given RMS Voltage:
Given: VRMS(V) = 230V.
Peak to peak voltage, Vp-p(V) = 2.828427 * VRMS(V)
Vp-p(V) = 2.828427 * 230
Vp-p(V) = 650.54V.
- Determine the RMS Voltage if the Peak-to-Peak Voltage is Known:
Given: Vp-p(V) = 1000V.
Peak to peak voltage, Vp-p(V) = 2.828427 * VRMS(V)
VRMS(V) = Vp-p(V) / 2.828427
VRMS(V) = 1000 / 2.828427
VRMS(V) = 353.55V.
Applications and Considerations:
- Audio Engineering: Understanding the peak-to-peak voltage helps in designing audio amplifiers and speakers to handle maximum signal levels without distortion.
- Radio Communications: Peak-to-peak voltage measurements are crucial for adjusting transmitter power and ensuring clear signal transmission.
- Oscilloscopes: Technicians and engineers use the peak-to-peak voltage to calibrate and adjust oscilloscopes for accurate waveform measurements.
Peak Voltage Vp and Peak to Peak Voltage: