History of Electrical Engineering:
In this we have given 14 electrical scientists you may get excited about their stories,
Electrical engineering has an evolution which was done by few people who needs to be remembered. Among them here are some. We show our gratitude for their effort and work. Hats off to them.
- William Gilbert(1540–1603): He was an English physician. He is the founder of magnetic science and he published De Magnete in 1600.
- Charles A Coulomb (1736–1806): He was a French engineer and physicist. He published the laws of electrostatics in between 1785 and 1791. Unit of charge Coulomb was named after him.
- James Wyatt(1736–1819): He was an English inventor. He developed the steam engine. Unit of power is named after him.
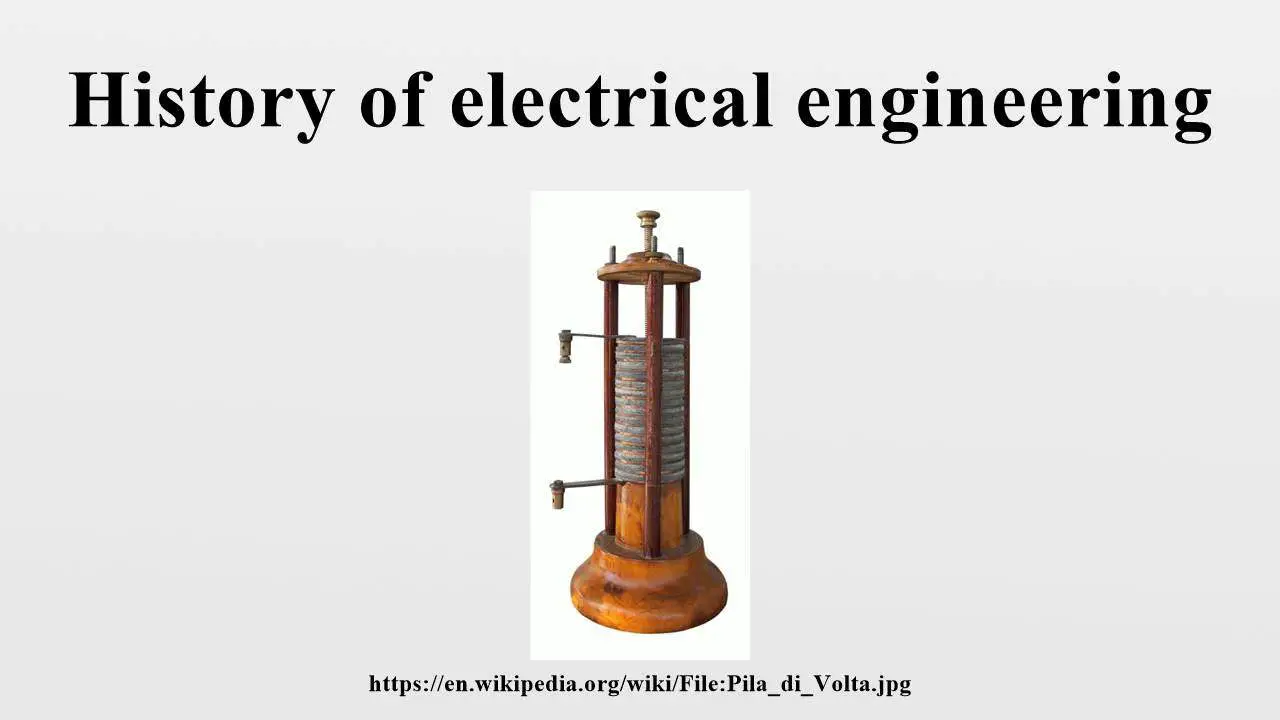
- Alessandro Volta(1745–1827): He was an Italian physicist. He discovered the electric pile. His name is used to represent the unit of electric potential and the alternate name of this quantity (voltage).
- Hans Christian Oersted(1777–1851): He was a Danish physicist. He discovered the connection between electricity and magnetism in 1820. His name is used to represent the unit of magnetic field strength.
- Andr´e Marie Amp`ere(1775–1836): He was a French mathematician. He was also a chemist and physicist. The relationship between electric current and the magnetic field was first electrically quantified by him. His name is used to represent the unit of electric current.
- Georg Simon Ohm(1789–1854): He was a German mathematician. He investigated the relationship between voltage and current and quantified the phenomenon of resistance. First results of his work were published in 1827. Unit of resistance is named after him.
- Michael Faraday(1791–1867): He was an English experimenter. He demonstrated electromagnetic induction in 1831. The beginning of the age of electric power was marked by his electrical transformer and electromagnetic generator. Unit of capacitance was named after him.
- Joseph Henry(1797–1878): He was an American physicist. He discovered self-induction at around 1831. Unit of inductance was named after him. The essential structure of the telegraph was first recognized by him. Later on, Samuel F. B. Morse perfected it.
- Carl Friedrich Gauss(1777–1855): He was a German mathematician. He and Wilhelm Eduard Weber (1804–1891), a German physicist, first published the measurement of earth’s magnetic field in 1833. Unit of magnetic field strength is Gauss, while the unit of magnetic flux is Weber.
- James Clerk Maxwell(1831–1879): He was a Scottish physicist. He discovered the electromagnetic theory of light. He also discovered the laws of electrodynamics. Maxwell’s equations are the base of the modern theory of electromagnetics.
- Ernst Werner Siemens(1816–1892) and Wilhelm Siemens (1823–1883), both were German inventors and engineers. They perfected electrical science and contributed to the invention and development of electric machines. Their name is used to represent the modern unit of conductance.
[wp_ad_camp_1]
- Heinrich Rudolph Hertz(1857–1894): He was a German scientist and experimenter. He discovered the nature of electromagnetic waves. He then published his findings in 1888. The unit of frequency is named after him.
- Nikola Tesla(1856–1943): He was a Croatian inventor. But in 1884 he immigrated to the United States. He invented poly-phase electric power systems. The modern AC electric power system and induction motor was his work. The unit of magnetic flux density is named after him











![What is Arc Chute? Types, Working Principle [Video Included] arc chute working priciple](https://www.electrical4u.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/arc-chute-218x150.png)
Interesting information about electrical engineering history