Histoy of MOSFET
In 1942 computer takes 70 hours to calculate the π value up to 2037 digits. Now the smart phone can do this task in 0.5 sec this miracles growth in speed is made by a tiny device inside the electronic gadget called a transistor typically a specific transistor called MOSFET.
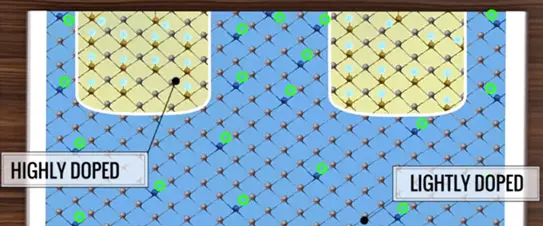
MOSFET is an electronically driven switch which allows and prevents the flow of current without any moving parts. MOSFET is also made of semiconductor material such as silicon. In pure semiconductor has very low conductivity. However when you introduced to control the amount of impurities is semiconductor material its conductivity increases sharply its procedure for adding impurity is called Doping.
First understand the internal structure of silicon and also the impurity known as doping. Pure silicon does not have electron because of its conductivity is very low. When we inject impurity as an extra electron into the silicon the conductivity of the resultant material increases dramatically this is known as N-type doping.
We can also increase impurity of adding fewer electrons it also increases the conductivity of pure silicon. This is known as P-type doping.
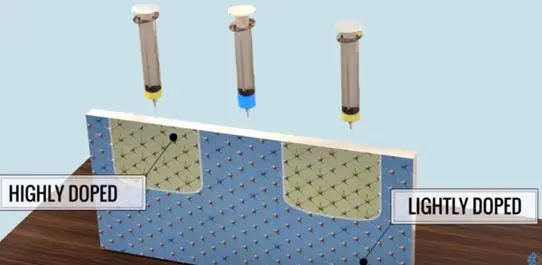
When the concentration of impurity is lowered the doping is set to low or light. If it is higher the doping is preferred as high or healthy.
Working of MOSFET
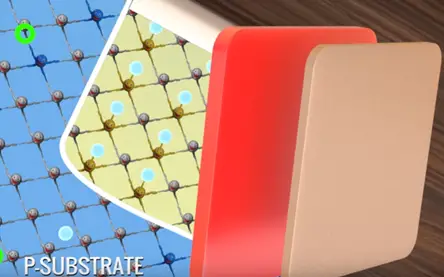
If we doping silicon in a wafer type in falling manner we will get a basic structure of MOSFET.
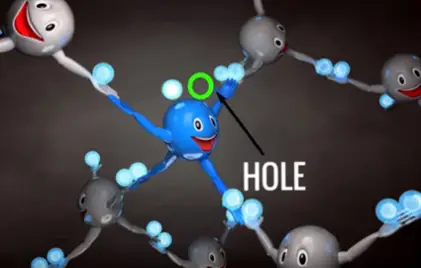
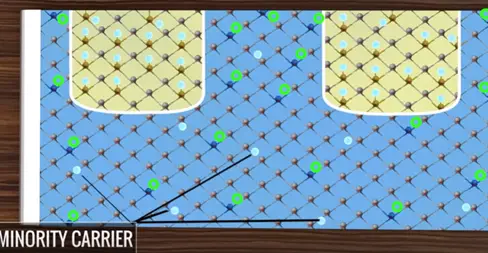
It is intensity known that P- region there are very few electrons that capable of conductivity electricity we called them minority carriers.
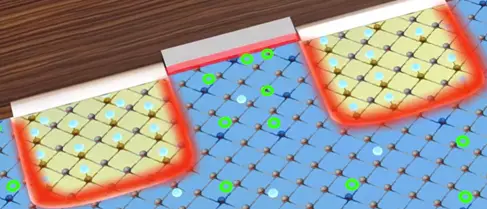
Whenever the PN junction is formed excess electron in the N-region have the tendency to occupy the holes in the P-region this means the PN junction boundary naturally becomes free of holes or free electrons. This region is called depletion region.
The same phenomena is happens in the PN junction of the MOSFET.
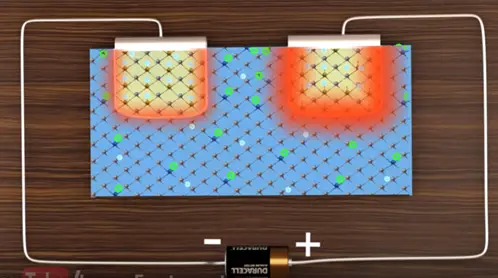
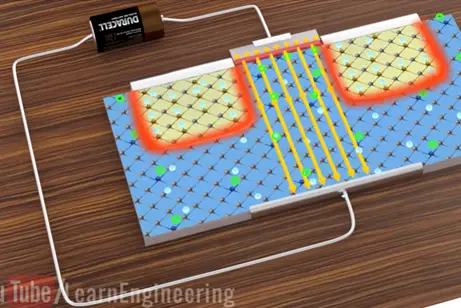
Now let’s connect the power source across the MOSFET.
On the right side the PN junction the electrons are attracted to the positive side of the call and the holes are moved away. In depletion region of the right side increased due to power source. This means there is no electrons will flow in MOSFET. In this simple arrangement of MOSFET will not work.
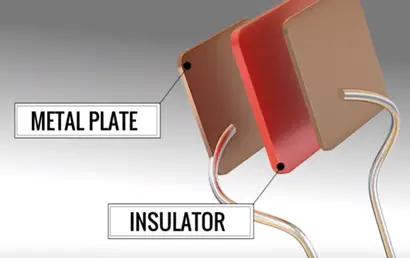
Let’s see how it is possible to have electron flow in the MOSFET using a simple technique. For this it required a capacitor.
Let’s see the working of capacitor inside capacitor we can see two parallel metal plates operated by an insulator.
When you apply a DC power source the positive terminal of the call attracts electrons in metal plate. These electrons are accumulating in the other side metal plate.
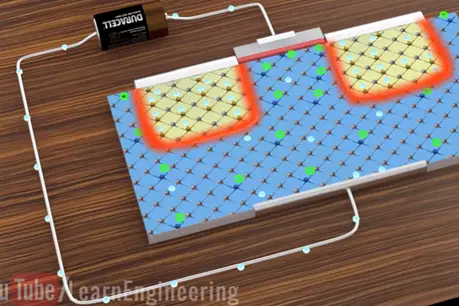
These accumulation charges create electric field between the plates. Let’s replace one plate of capacitor with the P-type substrate of the MOSFET.
When we connect the power source across the MOSFET
The electrons will leave the metal plate in MOSFET these electrons will be dispersed into P substrate positive charge generated in the metal plate due to electron displacement will generate electric field. Remember there are some free some free electrons even in the P type region.
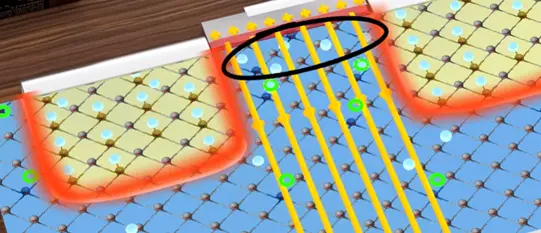
The electric field produced by the capacitive action will attract the electron to the top. We will assume electric field generated is quite strong. Then absorb the electron flow. At the top region it becomes over crowded with the electrons all the holes they are filled.
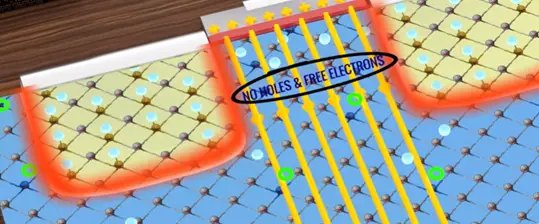
Below this region all the holes are filled but there is no free electron. This region becomes the new depletion region.
This process breaks the depletion region barrier channel for the flow of electrons created.
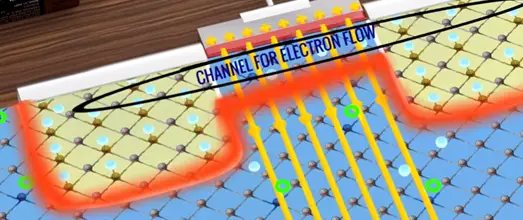
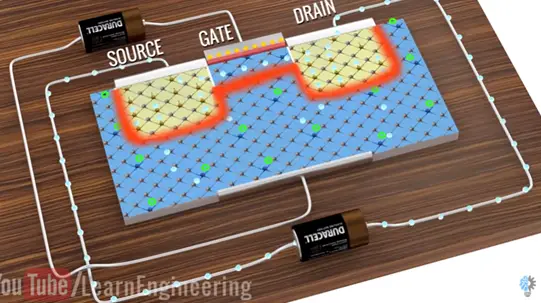
We can easily correlate the name of the transistor terminals with the electron flow.
If the voltage is applied is not enough the electric filed will be week it won’t be a channel formation and no electron will flows. This by controlling the gate voltage we will be able to turn ON/OFF MOSFET.
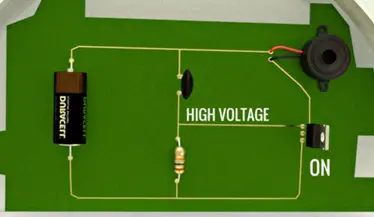
In real life MOSFET acts as a switch. Consider heat based fire alarm.
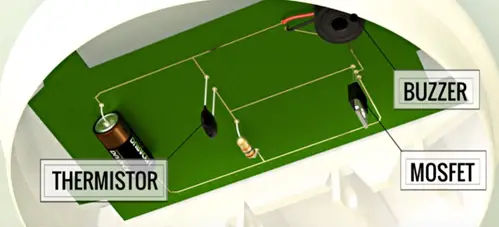

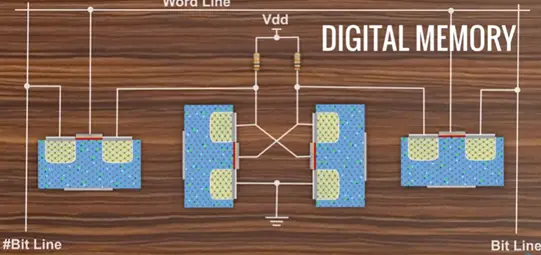
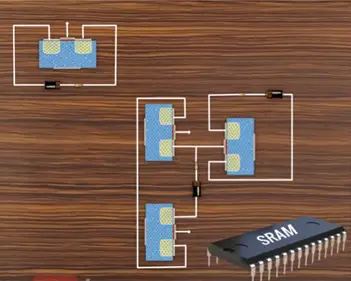
MOSFET open the digital memory and digital processor four MOSFET combine together and form basic memory element of static RAM. At the lowest level MOSFET are formed together as logic gates.
The combined to form a processing units as thousands of logical and arithmetic operations as its chips and millions of MOSFET are fabricated in the wafer.
Image Credit: https://www.youtube.com/user/LearnEngineeringTeam