What is MCCB – Moulded case circuit breaker:
Moulded case circuit breaker is a full form of MCCB in electrical. MCCB is an automatic electrical device used to protect the electrical equipment from overload, short circuit, instantaneous over current and earth fault. It is an advanced version of MCB (Miniature circuit breaker). It is available from 32 Amps to 1600 Amps with the voltage range of 230V to 1.1kV.
The main advantage of MCCB (Moulded case circuit breaker) is that we can tailor it as per our requirement by installing with new future such as remote closing, UV trip etc. It is the best replacement for an air circuit breaker in terms of cost as well as better function. Also, you can adjust the current setting as well as the time setting in the moulded case circuit breaker.
Single Line Diagram:
Moulded case circuit breaker is indicated by a small curve followed by the two lines

The input and output of the moulded case circuit will be bottom and top side.
Construction:
MCCB Consists of 9 different parts such
- Arc chute
- Moving Contact
- Operating mechanism
- Base cover
- Terminal Connector
- Overload trip or Bimetallic contact
- Handle knob
- Manual trip button
- CT – Current Transformer assembly
Let’s see the detailed explanation of the construction of MCCB. Before refer the picture.
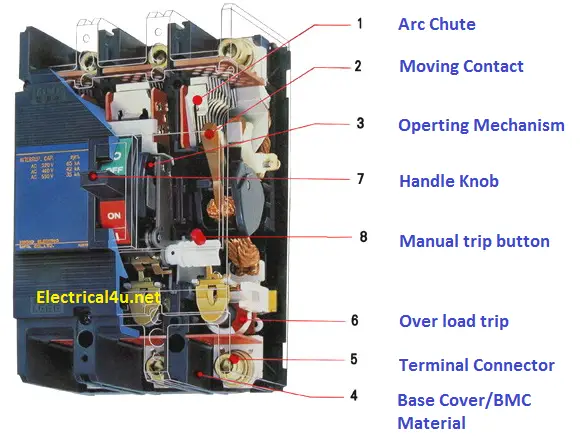
Arc chute:
It is a stack of mutually insulated parallel metal plates that used to divide the arc being developed in the moulded case circuit breaker. Arc chute material is made up of steel and glass fiber material.
Moving contact:
An electrolyzed brass material is used as a moving contact. The MOC (Material of Construction) of the moving contact should be high arc resistance, corrosion resistance, low resistivity etc. The MOC decides the life span of the MCCB.
Operating mechanism:
It deals with the contact opening and closing process. The speed of the operating mechanism does not depend on how fast the handle is moved. It is called a quick make and quick break.
It will be associated with the relay operating mechanism.
Also, breakers are designed with the test mechanism which allows the breaker to trip manually.
Base Cover:
A closed assembly of glass-fiber reinforced thermoset polymer material primarily used as a base cover of the Moulded case circuit breaker. It gives better mechanical strength. All the parts of the MCCB will be mount inside of these covers.
Terminal connector
The terminal connector is a bolt assembly, made up of steel material. It is used to connect the external circuit with the MCCB. Generally, Allen’s head (hexagonal) with 8.8 Ton torque range bolts is used as a terminal connector. It ensures there is no loose contact between the terminal.
If the rating of the MCCB is more than 400Amps means, the terminal connector will be equipped with an assembly called spreader links.
They are used to connect MCCB with the higher rating cables since the cable size will be bigger for the higher current ratings.
Bimetallic Contact:
A temperature-sensitive component, the composition of steel and copper material is used as bimetallic contact. Bimetallic contact is assembled in series with the line current.
Hence, the full line current of the breaker always will be passed through the bimetallic contact.
It is used to trip the breaker under an overload condition.
Handle Knob:
It is used to close or open the contact manually. Also, you cannot force to stop the breaker tripping by holding knob at the top side. It is called a free trip.
Handle knob indicates the breaker status, whether it is in ON position or OFF position.
If the handle is in the upward direction, it is called ON position, if it is in the downward position, the same called off position. If it is tripped, then the handle would be in the center position.
Manual trip button:
A red color button that is associated with the operating mechanism is called a manual trip button. It is mainly used to trip the breaker manually for testing purposes.
Current Transformer & Trip unit assembly:
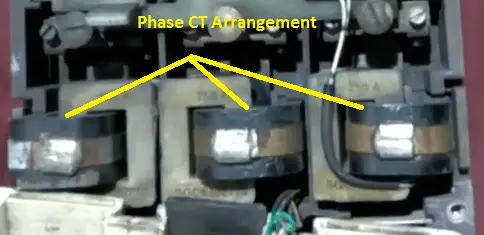
A set of current transformer is mount inside of the breaker as shown in the above-mentioned figure,
The output of the CT will be connected to the relay tripping unit. It is the brain of the MCCB.
The tripping unit contains an electromagnetic coil associated with the tripping plunger. The electromagnetic coil is used to trip the breaker with a predefined time delay during a short circuit, earth fault, and instantaneous fault condition.
Working Principle:
The MCCB working principle is simple. Let us take three different fault conditions such as Overload, short circuit, and earth fault.
Overload trip
A flow of current that exceeds the rated current with predefined time limit such a fault is called overload. Actually, it is not a fault, it is a condition.
The bimetallic contact involves in overload operation of the breaker; under the normal condition, it allows the current flow. If the current flow exceeds the predefined value, then it will get bend and finally, it will engage the tripping mechanism. The trip mechanism opens the breaker. Refer to the picture below mentioned
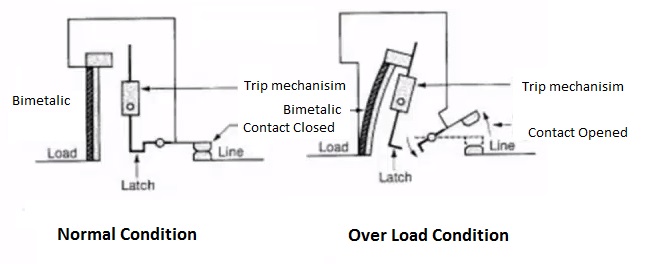
Also, bimetallic contact will not allow the breaker to reset instantly. Since it takes some time to reach its original state.
Over Load, the setting will be 80% to 100% of the full load current and the dame depending upon your load demand. But the time delay will be 10 to 15secs.
Short circuit / instantaneous/earth fault trip:
An electromagnetic coil involves short circuit/instantaneous/earth fault protection of the breaker. Under normal conditions, the CT generates less current hence the electromagnetic field is generated by the coil is not enough to pull the plunger. Therefore, the breaker does not trip.
During short circuit or instantaneous fault conditions, the CT generates high current and the coil creates a strong magnetic field. Hence the coil pulls the plunger and it will trip the circuit instantly.
The typical setting of a short circuit will be 2.5Times of the overload setting and the time delay will be 0.2 to 0.5 secs.
The typical setting of an instantaneous fault will be 4 Times of the overload setting and the time delay will be zero.
Earth Fault leakage trip:
Earth leakage protection is quite different from other protection. It a tailor-made one. It requires additional CT which has to be installed in the moulded case circuit breaker.
The output of the current transformer will be connected in star. Under normal conditions, the current flow through the star’s neural point will be zero. if the leakage found in the line means, the same will be sensed at the star terminal. if the leakage flow is higher than the allowable limit means, the MCCB trip the circuit.
Types of MCCB
According to the tripping types, the MCCB is divided into six categories.
TypeB: They are operating at the fault current reaches 3 to 5 times the full load current. It is used for domestic applications such as resistive load, lighting loads, etc. The available operating time of this beaker is 0.04 to 15 seconds
TypeC: Type C breaker specially used for inductive loads, such as transformers, welding machines, electromagnets etc. it has an operating range of 5 to 8 times the full load current with the time delay of 0.04 to 5seconds.
TypeD: Suitable for heavy starting current applications such as motors, pumps, lifts, etc. It has an operating range of 10 to 15 times with the time duration of 0.04 to 3 seconds
TypeK: Operates when the current goes to 8 to 10 times its full load current. Operating time for type K MCCB is 0.04 to 5 Seconds. They are the best suitable feeder protection.
TypeZ: Type Z MCCBs are very sensitive and they can able to allow 1.5 to 3 times the full load current. Type Z is suitable for electronics load, whereas high-speed tripping required.
MCCB rating
The manufacture provides some technical data that is used to understand the characteristics of the MCCB. Let us see.
Inm – rated Frame current => the maximum allowable current through the MCCB whereas MCCB operates under the stable region.
In => Rated current => Functional tripping range of the breaker.
Ui => Rated Insulation Voltage => the maximum allowable voltage ranges of the breaker.
Ue => Rated Voltage => Functional voltage of the breaker
Uimp => Rated Impulse Withstand voltage => Surge Voltage of the MCCB, the standard size for impulse testing is 1.2/50µs
Ics => Short circuit Breaking Capacity => The maximum amount of short circuit current where the breaker can break the circuit without physical damage.
Ics => Unlimited short circuit breaking capacity => The maximum breaking capacity of the MCCB whereas the MCCB can break the circuit with the physical damage. Beyond that limit, it will not operate
Advantage
- Occupy less space in the electrical panel
- Cheaper than ACBs
- Adjustable current settings
- Maintenance-free
- Fault clearing times are faster than the fuse units.
- No need to keep the spares, hence the inventory will be reduced.
- Suitable for industrial and commercial applications
Disadvantages
- LISG fault needs to tailor it.
- Needs additional add-on for getting feedback from the MCCB.
- Not suitable domestic application.
- Life span is less as compared with ACBs
- Not suitable for high voltage applications.
Applications:
- I have used it for many induction motor’s starters such as star-delta, DOL starter, Soft starter etc,
- Panel incomer applications,
- Distribution feeder
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can we use it for the DC application?
Yes, we can use it, but it will not trip on short circuit fault.
2. Best suitable type MCCB for the star-delta starter?
Type D, since the operating range is high, they can tolerate the high starting current of the induction motor.
3. How to choose the MCCB?
While purchasing MCCB, you have to take care of rated full load current, types of mccb, Ics.
4. Who is the best manufacture of MCCB?
Siemens is the best one. I have used in my many applications, they are user friendly.
5. How to reset the MCCB:
While tripping the MCCB, the handle knob will be in the middle position, in order to reset the breaker, pull the knob at the downside. It will get reset.
If you have any questions, leave a comment below…
Image Source: ATCAdvance



![What is Normally Open & What is Normally Closed [Video Included] What is NO and NC](https://www.electrical4u.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/What-is-NO-and-NC-218x150.png)






Mentioned type is for MCB or MCCB.
Yes SOMU… MCCB Only..As per IEC, the type is same..MCCB is an advanced version of MCCB..
Hi,
Very well explained about MCB types and their uses and types, got new insights from your article thanks for sharing.
Is it possible to parallel 2 pole of MCCB to increase current caring capacity?
How can we use MCCB for DC current,
No, you can not use, since of one of the MCCB trips means, another have a chance to over rapidly which increase the possibility of MCCB failure(Late trip). For using DC, you have to buy DC MCCB only, you can not use AC MCCB in DC circuits.
Thanks for the crystal clear explanation, I learned a lot in this article. Thank you
Our Mccb got to be tripping continuesly even all load in off condition. We can’t able to find.
What is the reason?
It could be mechanism problem. please open and reset the mccb manually.
Need a requirement of Type D for 160A from Schneider make.
Micrologic 2.2 will meet the category D requirement , Kindly confirm
why we cannot use mccb in DC side please give me explanation